I ran into this same problem when I deployed my application. There were several problems on my end 
I went through this page very carefully: ASP.NET Core: Publishing to IIS
First, I didn’t have all parts of the .NET Core Windows Server Hosting bundle installed. I ended up doing a fremework-dependent deployment instead of a self-contained deployment. We have a lot of apps and don’t want/need each on their own versions of .net core. There would be way too many versions of .net on the box.
Also, note that if your admins performed any updates/upgrades to the server, they could have jacked up your ASP.NET Core installation (see ASP.NET Core: Publishing to IIS troubleshooting section)
Then, I had to fix my web.config… here is my working published web.config:
I didn’t publish as an *.exe, I did *.dll (notice my arguments value). Also, my processPath is set to «dotnet».
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<add name="aspNetCore" path="*" verb="*" modules="AspNetCoreModule" resourceType="Unspecified" />
</handlers>
<aspNetCore processPath="dotnet" arguments=".DT.Web.dll" stdoutLogEnabled="false" stdoutLogFile=".logsstdout" forwardWindowsAuthToken="false" />
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Also, ensure that your project.json options are all set compatible with your server environment (see ASP.NET Core: Publishing to IIS troubleshooting section)
Here is a copy of the of my project.json if it can be of any help:
{
"version": "2.0.1.0",
"dependencies": {
"DT.Common": "2.*",
"DT.Configuration": "2.*",
"DT.Services": "2.*",
"DT.Web.ViewModels": "2.*",
"Microsoft.ApplicationInsights.AspNetCore": "1.0.2",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.OpenIdConnect": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Tools": {
"version": "1.1.0-preview4-final",
"type": "build"
},
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration.Tools": {
"version": "1.1.0-preview4-final",
"type": "build"
},
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.Kestrel": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.Kestrel.Https": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Session": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.StaticFiles": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.SqlServer": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Abstractions": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.FileExtensions": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Debug": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Options.ConfigurationExtensions": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.Graph": "1.1.1",
"Microsoft.IdentityModel.Clients.ActiveDirectory": "3.13.6"
},
"tools": {
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration.Tools": "1.1.0-preview4-final",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Tools": {
"version": "1.1.0-preview4-final",
"imports": "portable-net45+win8+dotnet5.6"
},
"Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.SqlConfig.Tools": "1.1.0-preview4-final"
},
"frameworks": {
"netcoreapp1.1": {
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8"
],
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.NETCore.App": {
"version": "1.1.0",
"type": "platform"
}
}
}
},
"buildOptions": {
"emitEntryPoint": true,
"preserveCompilationContext": true
},
"runtimeOptions": {
"configProperties": {
"System.GC.Server": true
}
},
"publishOptions": {
"include": [
"wwwroot",
"views/**/*.cshtml",
"appsettings.json",
"appsettings.*.json",
"web.config"
]
},
"scripts": {
"prepublish": [ "bower install", "gulp buildprod" ],
"postpublish": [ "dotnet publish-iis --publish-folder %publish:OutputPath% --framework %publish:FullTargetFramework%" ]
}
}
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
User-1044541387 posted
My webpage was working fine up until last Friday when I started to receive this error when I accessed the homepage:
502 — Web server received an invalid response while acting as a gateway or proxy server.
There is a problem with the page you are looking for, and it cannot be displayed. When the Web server (while acting as a gateway or proxy) contacted the upstream content server, it received an invalid response from the content server.
I have looked in C:inetpublogs but there doesn’t seem to be a FailedReqLogFiles folder.
In the Event Viewer Logs I see the following error and information messages:
- Server «My Server» in server farm «My Server Farm» is being marked unhealthy due to health check status code failure
- Server farm «My Server Farm» has reached its minimum server threshold. No more servers will be marked unhealthy until the number of healthy servers increases.
- Unable to open the Server service performance object. The first four bytes (DWORD) of the Data section contains the status code.
Has anyone encountered similar before? If anyone has any tips/advice as to how to resolve I’d be very grateful. Thanks.
When deploying an ASP.NET Core application to IIS, you may find IIS returning HTTP Error 502.5 instead of your web page.
I recently hit this problem after manually modifying the web.config file. Fortunately, the problem is easy to fix.
In this post, we see two different causes of this error, two different solutions for the first cause, a solution for the second cause, and learn what needs to be in web.config for ASP.NET Core to operate.
The Error
Here is a screenshot of the HTTP Error 502.5 - Process Failure error. You’ll see this, in your browser, when making a request to your ASP.NET Core application, after deployment, if you have this issue.
Why do I get the error?
The HTTP Error 502.5 - Bad Gateway and HTTP Error 502.5 - Process Failure error messages occur in ASP.NET Core when IIS fails to execute the dotnet process.
I’ve seen this error happen for two different reasons:
- .NET Core Runtime is not installed
web.configfile has not been transformed
Fix 1a: Install the .NET Core Runtime
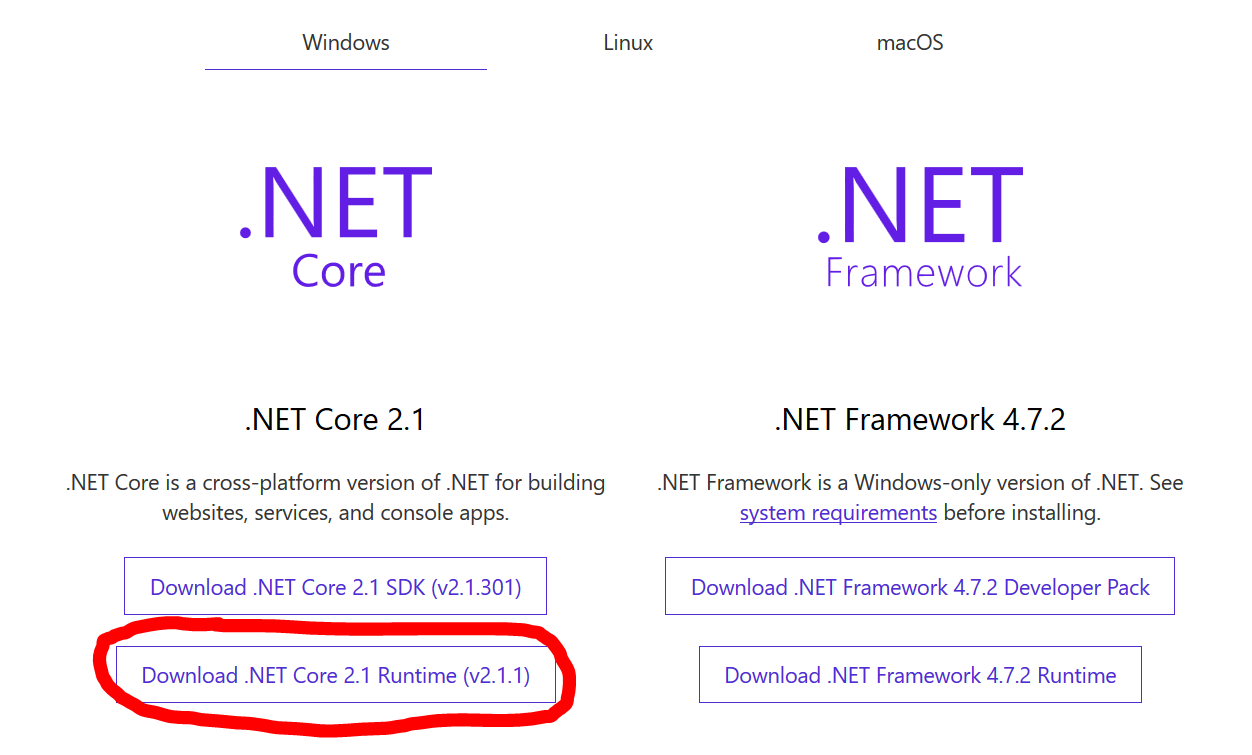
The most common reason for this to occur is when you haven’t installed the .NET Core runtime on the server.
You can download the latest .NET Core runtime from Microsoft’s .NET download page.
For Windows, you’ll usually want the latest .NET Core runtime (currently v2.1.1), as highlighted in the following screenshot:
This will get you the Windows Hosting Bundle Installer, which will install both the x86 and x64 runtimes on Windows Server.
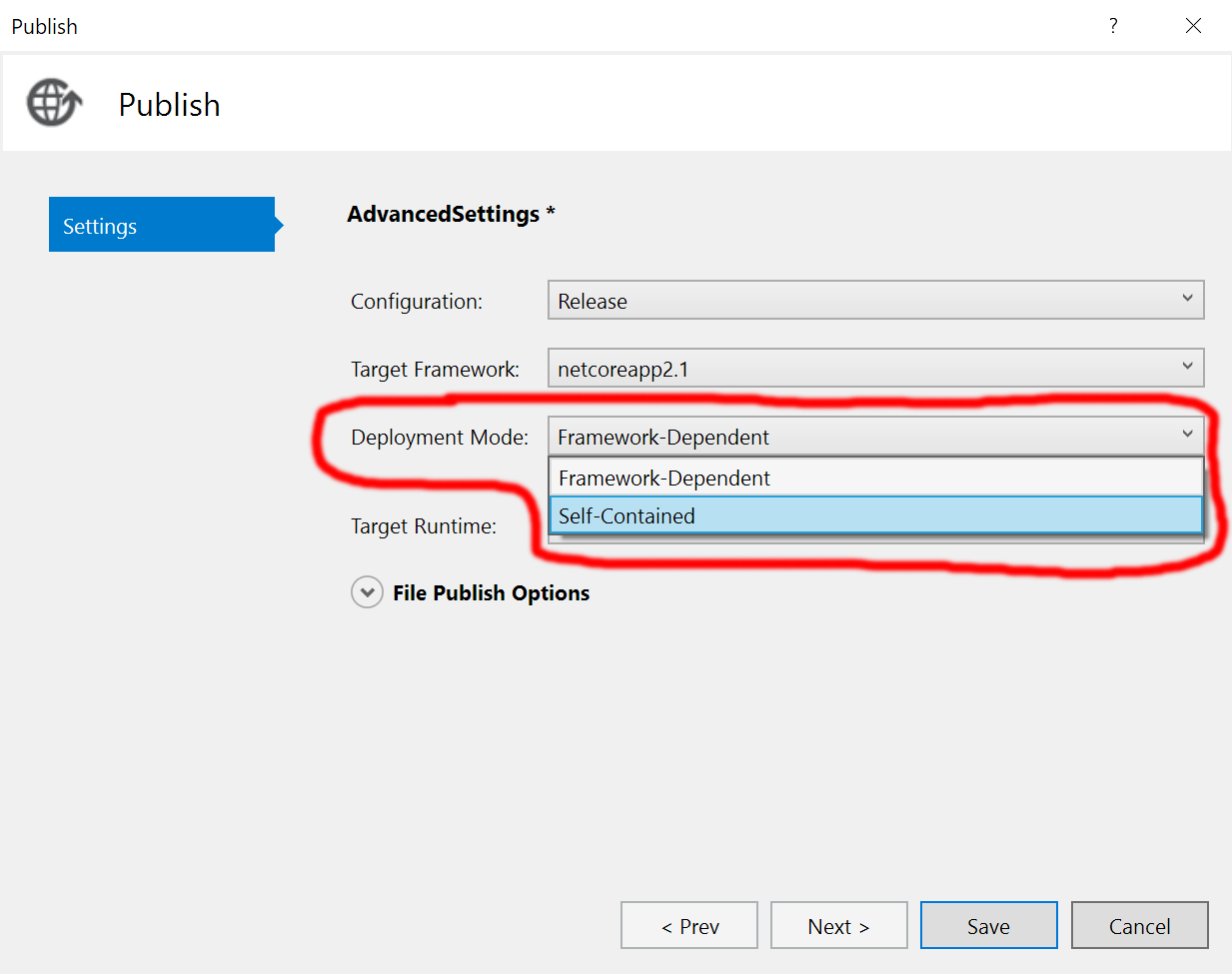
Fix 1b: Publish a Self-Contained Deployment
If you don’t want to install the .NET Core Runtime. An alternative for .NET Core web applications is to publish them in the Self-Contained deployment mode, which includes the required .NET Runtime files alongside your application.
You can select this option from the advanced publish settings screen in Visual Studio:
If you go with this option, you’ll also need to choose a target runtime: win-x86, win-x64, osx-x64, or linux-x64. Because self-contained deployments are not portable.
Fix 2: Transform your web.config file
Another reason for this error to occur is when you deploy an untransformed web.config file.
This is likely to be your issue if you had a previously working web application and merely deployed a new version of it.
ASP.NET Core Web Config
In ASP.NET Core applications, the web.config file contains a handler that directs requests to the AspNetCoreModule and an aspNetCore element that defines and configures the ASP.NET Core process to execute your web application.
Here is a minimal web.config file for an ASP.NET Core application:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<handlers>
<add name="aspNetCore" path="*" verb="*" modules="AspNetCoreModule" resourceType="Unspecified" />
</handlers>
<aspNetCore processPath="%LAUNCHER_PATH%" arguments="%LAUNCHER_ARGS%" stdoutLogEnabled="true"
stdoutLogFile=".logsstdout" forwardWindowsAuthToken="false"/>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Note that it’s possible that you don’t have a web.config file in your ASP.NET Core project. If you do not, one will be generated for you when publishing the project, as IIS and IIS Express require a web.config file when hosting an ASP.NET Core web app.
The Issue
The untransformed web.config contains the variables %LAUNCHER_PATH% and %LAUNCHER_ARGS% rather than the correct paths. When IIS tries to run ASP.NET Core, it uses %LAUNCHER_PATH% and %LAUNCHER_ARGS% rather than the correct path and arguments.
To fix the HTTP Error 502.5 in ASP.NET Core, you need to transform the web.config and replace the untransformed web.config file on the IIS web server.
How do I transform web.config?
This transformation takes place when you choose to publish your web application. The transformed web.config ends up in the published output folder. Therefore, you simply need to publish your web application and copy the resulting web.config file onto the server.
In a transformed web.config file, the aspNetCore element will look something like this:
<aspNetCore processPath="dotnet" arguments=".MyApplication.dll" stdoutLogEnabled="true"
stdoutLogFile=".logsstdout" forwardWindowsAuthToken="false" />
%LAUNCHER_PATH% has been replaced by dotnet and %LAUNCHER_ARGS% has been replaced by the path to the main web application dll .MyApplication.dll.
Addendum
Update (4th July 2018): The same error occurs when the .NET Core Runtime is not installed. So, I have updated the article to include the solution to this more common issue as well.
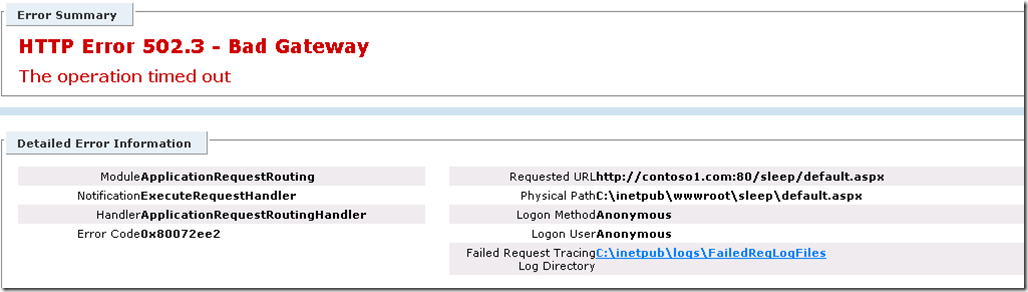
When working with ARR deployments one of the errors you might see is 502.3 Bad Gateway. The 502.3 means while acting as a proxy ARR was unable to complete the request to the upstream server and subsequently send a response back to the client. This can happen for multiple reasons including , failure to connect to the server , no response from the server, or server took too long to respond (time out).
For the purposes of this post we are going to look at a timeout error and the data that can be gathered to help isolate the cause.
If you are looking at this post then you probably have already seen this error or something similar. This is shown in the browser when detailed errors are enabled in IIS.
Another way to identify the source of the 502.3 is with Failed Request Tracing logs in IIS configured to capture Status code 502.
From the message the key details are the ErrorCode which you can use to map to to the Winhttp error message, which in this case is ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT ( Reference WinHttp Error Codes). You will also see in the next line that this is translated to “The operation timed out”. Note that both the 0x80072ee2 and 2147954402 map to the same error ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT.
Now that we know its a timeout we need to determine what type of timeout occurred. Here is a list of the timeouts that can occur in Winhttp ( which if you haven’t guessed already is what ARR uses to proxy requests)
- ResolveTimeout : This occurs if name resolution takes longer than the specified timeout period.
- ConnectTimeout : This occurs if it takes longer than the specified timeout period to connect to the server after the name resolved.
- SendTimeout : If sending a request takes longer than this time-out value, the send is canceled.
- ReceiveTimeout : If a response takes longer than this time-out value, the request is canceled.
To identify what type of timeout we can use Winhttp’s built in logging,These can be enabled from the command line on the ARR server using NETSH.
- Winhttp Traces:
Following the example below you can search your log for WinHttpOpenRequest to find your request. The calls to WinHttpSetTimeouts are setting the 4 timeout values based on your ARR time settings found in the Proxy Configuration page of your ARR Server Farm or in the Server Proxy settings. Next we find WinHttpSendRequest then WinHttpReceiveResponse , so we know we are now in the receive stage. Finally we see that the error in is in RecvResponse so we know this is a ReceiveTimeout. For a different failure such as ResolveTimeout we would not see the log make it to WinHttpReceiveResponse and the failure would be logged earlier.
10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpOpenRequest(0x35a970, "GET", "/sleep/default.aspx", "HTTP/1.0", "", 0x0, 0x00000080) ………… 10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSetTimeouts(0x2e42d80, 30000, 30000, 30000, 30000) 10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSetTimeouts() returning TRUE …………10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSendRequest(0x2e42d80, "Accept: */*rnAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflaternAccept-Language: en-CArnHost: contoso.com", 479, 0x0, 0, 0, 24794c0) …………10:24:15.397 ::Completing WinHttpSendRequest() with success; Request Handle = 02E42D80, Context = 024794C0, Buffer = 00000000 (0x0), Buffer Length = 0 10:24:15.397 ::WinHttpReceiveResponse(0x2e42d80, 0x0) ………… 10:24:15.397 ::sys-recver failed to receive headers; error = ? (1460) 10:24:15.397 ::ERROR_WINHTTP_FROM_WIN32 mapped (?) 1460 to (ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT) 12002 10:24:15.397 ::sys-recver returning ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT (12002) from RecvResponse() 10:24:15.397 ::sys-req completes recv-headers inline (sync); error = ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT (12002)
Now that we know this is receive timeout we can look at the content server and see how long the request took.
-
IIS logs on the Content Server:
Examine the IIS logs on the content server and check the sc-status and sc-win32-status and time-taken fields. This will give you an idea of whether the request processed successfully ( sc-status = 200) and the time-taken to see if this exceeds your ARR timeout and if this is the expected execution time for your web page . You can determine from this whether you need to troubleshoot a long running application or simply increase the ARR timeout settings. Checking the Win32 field for errors such as 1236 (ERROR_CONNECTION_ABORTED) or 64 (ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED) indicate that something happened on the network layer such as a connection reset.
Using our example the IIS logs here show that the Request took ~35 seconds (time-taken=35615) , the request was processed successfully on the server (sc-status=200) , but there was a problem sending the request (sc-win32-status=64) which means the connection was gone when the content server tried to send the request. This was because the client (ARR) has already timed-out and closed the TCP connection.
#Software: Microsoft Internet Information Services 7.0 #Version: 1.0 #Date: 2010-06-23 20:11:33 #Fields:date time cs-method cs-uri-stem s-port sc-status sc-substatus sc-win32-status time-taken 2010-06-23 20:11:33 GET /sleep/default.aspx 80 200 0 64 35615
Summary
So in this case we can see that the request took >35 seconds which is longer than the default timeout in ARR. When this occurs ARR ( or Winhttp underlying ARR) will close the connection to the content server which is what cause the Win32 error 64.
Now its up to you to determine whether its acceptable that your page is running for 35 seconds and you just need to increase time outs in ARR.
Since the application issues are beyond the scope of this blog I’ll leave you with two command lines for setting ARR timeouts for either a Server Proxy configuration or Server Farms.
Server Proxy : appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/proxy /timeout:»00:00:45″ /commit:apphost
Server Farm : appcmd.exe set config -section:webFarms /[name=’ArrFarm’].applicationRequestRouting.protocol.timeout:»00:00:45″ /commit:apphost
References
WinHttpSetTimeouts Function
Netsh Commands for Windows Hypertext Transfer Protocol (WINHTTP)
Failed Request Tracing in IIS (FREB)
UPDATE : New Post for Winhttp Tracing Methods
ARR on IIS.NET
The HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 502 Bad Gateway the server error is generated when an invalid response is received from a server. “502 Bad Gateway” is an HTTP status code that is defined and standardized with RFC. The “502 Bad Gateway” status code is defined in RFC 10.5.3.
HTTP uses status codes in order to provide information about the HTTP request between client and servers. Every HTTP request will return a HTTP status code like successful, failed, warning etc. The web is complex where some servers can make HTTP request to other servers too. “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” is a status code is mainly returned from a server where this server make some request to other server and can not get information and “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” is returned to the user.
“HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” Expressions
Even the canonical name for the “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” is used to express the error but there are other expressions to show this error. The following errors are generally used for the web.
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 502 Service Temporarily Overloaded
- Error 502
- Temporary Error (502)
- 502 Proxy Error
- 502 Server Error: The server encountered a temporary error and could not complete your request
- HTTP 502
- 502. That’s an error
- Bad Gateway: The proxy server received an invalid response from an upstream server
- HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway
- 502 Bad Gateway NGINX
- A blank white screen
Also other than different applications, software, operating systems uses the web for different purposes and can get “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error and print in different forms.
Windows Update requires to access th update servers which uses HTTP protocol to get information. The following error is returned which is related with the “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” status code.
0x80244021 error code or the message WU_E_PT_HTTP_STATUS_BAD_GATEWAY
Google provides a lot of web related services like Gmail, Google Search, Google Cloud, Google Drive Google Map etc. These service may return the “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error like below.

Linux Package Management command named “apt-get” uses HTTP in order to get recent package information and issue an “Error 502 Bad Gateway” error.
W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/trusty-security/main/source/Sources 502 Bad Gateway [IP: 91.189.91.13 80]

Linux Yum is another package manager for RPM based distributions and the HTTP 502 Error is expressed like below.
error was [Errno 14] HTTP Error 502: Bad Gateway

What Cause “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” Error?
“HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error is mainly related to the communication problems between intermediate servers. This means we have no control over this error.
- Browser Problem
- DNS Problem
- Firewall Configuration
- Internet Access
- Remote Website Problem
- Server Overload
- Website Software Error
Microsoft IIS “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” SubStatus Information
Microsoft IIS version 7.0 and later provides more detailed information about the “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error. It provides sub status code like “502.1”, “502.2” where every sub status code provides a specific case. This sub status information is not standard and only provided by the Microsoft IIS server.
- 502.1 – CGI application timeout.
- 502.2 – Bad gateway: Premature Exit.
- 502.3 – Bad Gateway: Forwarder Connection Error (ARR).
- 502.4 – Bad Gateway: No Server (ARR).
How To Fix /Solve “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” Error?
The “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error can be solved in different ways. Event the error is mainly related with the remote server or network there are some basic checks in order to fix or overcome this error.
Client Side Solutions
Reload URL is the first and most practical way to solve this error. “F5” or refresh button of the web browser can be used. Actually this will not fix the problem directly but just make a check if the problem continue or not.
Start New Session is another quick fix where previous sessions garbage will be omitted.
Clear your browser cache where outdated or corrupted files that are stored in the browser will be removed which can cause “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error.
Delete Cookies because previosuly stored cookies will use old values for an HTTP connection which can be cause of the “502 Bad Gateway” error.
Start Browsers in Safe/Private Mode which will omit previously craeted sessions and site preferences and prevent “502 Error”.
Try Different Browser where current browser may have problems. Try different browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Internet Explorer, Safari etc.
Disable Security Softwarewhere security software can block suspicious even legitimate action. Security software like Microsoft Defender, Kaspersky Endpoint Protection, Microsoft Forefront, TrendMicro Endpoint Protection etc. generally monitors network traffic and stops suspicious connections.
Restart Computer because some temporary configuration may prevent access to network and create “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error.
Restart Network Devices because they provide access to the internet and problem related with these devices will interrupt internet access which will cause “Bad Gateway Error”.
Change DNS Server is related with your computer or router. Some “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” errors are related with the DNS server errors or restrictions.
Server/Network Side Solutions
Contact website owner is responsible for the website you want to access. The problem may be related with the website architecture where you can contact website owner for the problem.
Contact ISP because the internet connection is provided by the ISP where it can be responsible for the “502 Bad Gateway” error.
Check origin server where it can be down for the CDN architecture.
Check Firewall Configuration and Logswhere server firewall can prevent some transfer between client or servers which will cause “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error.
Check Server Software where it may provide faulty responses or create unnecessary overload.
Check Server Services where services may be unreliable. If it is possible to restart the services and look for configuration changes.
Check Database Server because slow queries slowdown the websites and cause sow responses which will end with timeout and “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error.
Check Hosting Provider where there may a system or network problem related to the hosting which effects the web site.
Different “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” Error Pages
Below we will list some popular services “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway” error pages.
Cloudflare


GoDaddy



Microsoft IIS

Nginx