Автор:
Marcus Baldwin
Дата создания:
17 Июнь 2021
Дата обновления:
1 Июнь 2023
Содержание
- Возможные причины
- Возможные симптомы
- P219a Описание
- P219A Информация для конкретных марок
Возможные причины
Возможные симптомы
P219A Информация для конкретных марок
Content
- OBD-II Trouble Code — P219A — Data Sheet
- What does DTC P219A mean?
- What is the severity of this DTC?
- What are some of the symptoms of a P219A code?
- What are some of the common causes for the code?
- Diagnostics
- What are some steps to troubleshoot the P219A?
- Common mistakes
- Related codes
- Need more help with the P219A code?
OBD-II Trouble Code — P219A — Data Sheet
P219A — Bank 1 Air/Fuel Ratio Imbalance
What does DTC P219A mean?
This is a generic Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) applicable to many OBD-II vehicles (1996 and newer). This may include, but is not limited to, vehicles from Toyota, Dodge, Ford, Honda, Jeep, Chevy / Chevrolet, GMC, Ram, etc. Despite the general nature, the exact repair steps may vary depending on the model year, brand, models and transmissions.
When P219A is stored, it means the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected an air-fuel ratio imbalance for the engine block that contains cylinder number one.
The PCM uses data from heated exhaust oxygen sensors (sometimes called air fuel sensors) to monitor the air-to-fuel ratio for each row of engines.
Each oxygen sensor is constructed using a zirconia sensing element located in the center of a vented steel housing. Tiny electrodes (usually platinum) attach the sensor to the wires in the oxygen sensor harness connector and the connector connects to the controller network (CAN) that connects the oxygen sensor harness to the PCM connector.
Each oxygen sensor is screwed (or twisted) into the exhaust pipe. It is positioned so that the sensing element is closer to the center of the pipe. When waste exhaust gases leave the combustion chamber (through the exhaust manifold) and pass through the exhaust system (including catalytic converters), they pass through the oxygen sensors. Exhaust gases enter the oxygen sensor through specially designed air vents in the steel housing and swirl around the sensor element. Swirling ambient air is drawn in through the wire cavities in the sensor body to fill the tiny chamber in the middle of the sensor. Then the air (in a tiny chamber) is heated. This causes the oxygen ions to produce energy, which is recognized by the PCM as voltage.
Differences between the amount of oxygen ions in the ambient air (drawn into the O2 sensor) and the number of oxygen molecules in the exhaust cause the oxygen ions inside the O2 sensor to very quickly and intermittently bounce from one platinum layer to another. … As the pulsating oxygen ions move between the platinum layers, the output voltage of the oxygen sensor changes. The PCM sees these changes in the oxygen sensor output voltage as changes in the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The voltage outputs from the oxygen sensors are lower when more oxygen is present in the exhaust (lean state) and higher when less oxygen is present in the exhaust (rich state).
If the PCM detects an air-fuel ratio imbalance for a specific engine group, code P219A will be stored and a malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) may illuminate. Most vehicles will require several ignition cycles (on failure) to turn on the warning light.
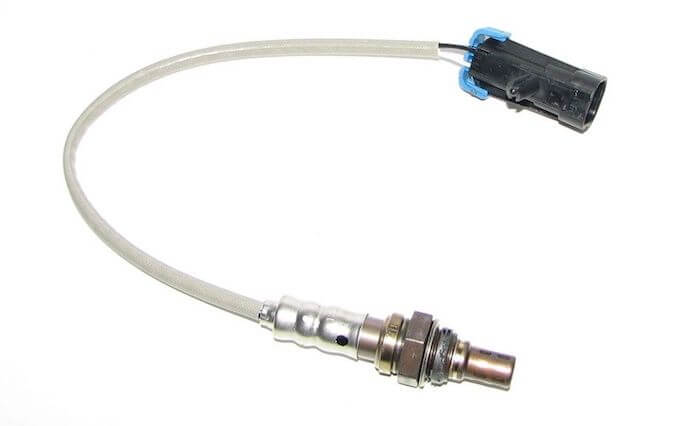
Typical oxygen sensor:
What is the severity of this DTC?
An incorrect air to fuel ratio can be the result of a lack of fuel or an excessive amount of air (vacuum). P219A should be classified as serious and should be addressed as soon as possible.
What are some of the symptoms of a P219A code?
Symptoms of a P219A trouble code may include:
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Lack of overall engine performance
- Stored Misfire Codes or Lean / Rich Exhaust Codes
- Service engine lamp will light up soon
- Leaks in the exhaust or intake system
- The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system is leaking or the valve is stuck open.
- Run out of fuel or low fuel pressure
- EVAP canister purge valve leak
- Ignition system
- Leaky or dirty fuel injectors
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
- Oil dipstick, tube or oil filler cap installed incorrectly
What are some of the common causes for the code?
Reasons for this code may include:
- Engine vacuum leak (large)
- Defective oxygen sensor / s
- Burnt, frayed, broken, or disconnected wiring and / or connectors
- Engine exhaust leaks
- Defective MAF or manifold air pressure sensor.
- Bad fuel pump or clogged fuel filter
- Leaks in exhaust or intake system
- The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system is leaking or valve stuck in the open position.
- Run out of fuel or low fuel pressure
- EVAP canister purge valve leak
- Leaky or dirty fuel injectors
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
- Oil dipstick, tube or oil filler cap installed incorrectly
Diagnostics
To diagnose DTC P219A, a technician must:
- Scan codes in ECM and view the stop data frame . P219A is usually accompanied by other trouble codes that can really help with the diagnosis.
- Check fuel pressure, PCV system operation.
- Inspect the position sensor throttle and take a look at the exhaust pipe and see if there are any traces of soot where the exhaust pipe exits.
- Check for leaks in the EVAP system.
- Perform a visual inspection of hoses, wiring and components, especially wiring oxygen sensor.
- If any of the above or swap tests show that one or more components are faulty, they should be replaced/repaired as needed to keep this code from returning.
What are some steps to troubleshoot the P219A?
All misfire codes, throttle position sensor codes, manifold air pressure codes, and MAF sensor codes must be reviewed before attempting to diagnose code P219A. The engine must also run smoothly and efficiently. If it is determined that a rich or lean mixture (with the engine) exists, this must be corrected as this could be the reason for the P219A being retained.
You will need a diagnostic scanner, digital volt / ohmmeter (DVOM) and reliable vehicle information source to accurately diagnose the P219A code.
You can save time by searching for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) that reproduce the stored code, vehicle (year, make, model, and engine) and symptoms found. This information can be found in your vehicle information source. If you find the right TSB, it can quickly fix your problem.
After you connect the scanner to the vehicle diagnostic port and get all stored codes and associated freeze frame data, write down the information (in case the code turns out to be intermittent). After that, clear the codes and test drive the car until one of two things happens; the code is restored or the PCM enters ready mode.
The code can be more difficult to diagnose if the PCM goes into ready mode at this point because the code is intermittent. The condition that led to storage of P219A may need to worsen before an accurate diagnosis can be made. If the code is restored, continue diagnostics.
You can get connector views, connector pinouts, component locations, wiring diagrams, and diagnostic block diagrams (related to the code and the vehicle in question) using your vehicle information source.
Visually inspect the associated wiring and connectors. Repair or replace cut, burnt, or damaged wiring.
If the engine runs normally and the P219A / P219B code continues to be reset, start the engine and allow it to reach normal operating temperature. Let the engine idle (in neutral or parking). With the scanner connected to the vehicle diagnostic port, observe the oxygen sensor input in the data stream. Narrow down your data stream to include only relevant data for a faster response.
If the oxygen sensors are operating normally, the voltage across the oxygen sensors upstream of the catalytic converter will cycle continuously from 1 to 900 millivolts when the PCM enters closed loop mode. The post-cat sensors will also cycle between 1 and 900 millivolts, but they will be set at a certain point and remain relatively stable (compared to pre-cat sensors). Oxygen sensors that are not working properly should be considered defective if the engine is in good working order.
- In most cases, you will fix this code by fixing a rich or lean engine.
Common mistakes
The following are some of the most common mistakes a technician can make when diagnosing a P219A code:
This generic diagnostic trouble code (DTC) applies to many OBD-II vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards, and includes a variety of makes such as Toyota, Dodge, Ford, Chevy, Honda and Jeep. While the diagnosis is generic in nature, exact repair steps may vary depending on the year, make and model of the vehicle. Furthermore, powertrain should also be taken into consideration when attempting repairs.
When a code P219A is stored in the powertrain control module (PCM), it means that the PCM has detected an air to fuel ratio imbalance for the bank of the engine which contains the number one cylinder. This can be caused by faulty oxygen sensors or other components related to air intake and fuel delivery in this particular engine. Proper diagnosis and repair of these issues should be done by a certified mechanic as soon as possible in order to avoid further damage due to incorrect functioning.
The PCM monitors the air to fuel ratio for each engine bank by utilizing data from heated exhaust oxygen sensors, also known as air fuel sensors. This method is used in order to ensure optimal performance and efficiency of the engine. The heated exhaust oxygen sensor helps provide information on how much oxygen is present in the vehicle’s exhaust system, which can then be compared against what was expected based on the computer-controlled fuel injection system. Through this process, any inconsistencies or issues are identified in real time and corrective measures can be taken swiftly.
The oxygen sensor is a device comprised of a zirconium dioxide sensing element housed in a vented steel housing, with tiny platinum electrodes connecting it to the oxygen sensor wiring harness connector that plugs into the controller area network (CAN) and further connects the harness to the PCM connector. This design allows for efficient communication between all necessary components.
The oxygen sensor is often threaded or studded into an exhaust pipe in order to ensure that the sensing element is close to the center of the pipe. As spent exhaust gases leave the combustion chamber and pass through the remainder of the exhaust system, they are directed over these sensors. To facilitate this process, vent holes are incorporated within the steel housing of each sensor so that swirling ambient air can enter it. This air ultimately fills a tiny chamber inside where it is heated, which causes oxygen ions to produce energy registered by a PCM as voltage.
The variations of oxygen ions between ambient air and the exhaust cause a swift, repetitive motion inside an O2 sensor. As these ions shift between the platinum layers, changes in output voltage are seen by the PCM. This allows for monitoring of concentration levels as lean or rich conditions based on the voltage signals sent from the oxygen sensors; higher outputs indicate lower concentrations while lower outputs signify richer concentrations.
If the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects an imbalance in the air to fuel ratio for a particular bank of the engine, it will store code P219A and may illuminate a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). In most vehicles, multiple ignition cycles with a failure are needed before MIL illumination.
What is the severity of this DTC?
It is important to recognize that an incorrect air to fuel ratio can be the result of either excessive air or insufficient fuel. The code P219A should always be considered severe and rectified quickly in order for it not to cause any further issues. Failure to do so could result in serious engine damage and costly repairs.
You’ll likely see symptoms of a P219A trouble code whenever your engine light comes on:
- Diminished fuel efficiency
- The lack of general engine performance
- Lean or Rich Misfire Codes
- Service engine soon lamp illumination
What are some of the common causes of the code?
Causes for this error code may include:
- Engine vacuum leak (large)
- Defective oxygen sensor/s
- Burnt, chafed, broken, or disconnected wiring and/or connectors
- The engine is leaking smoke.
- A mass air flow sensor or manifold air pressure sensor that’s faulty
- Bad fuel pump or clogged fuel filter
What are some P219A troubleshooting steps?
Before attempting to diagnose a code P219A, it is important to ensure that all misfire codes, throttle position sensor codes, manifold air pressure codes and mass air flow sensor codes have been addressed. Furthermore, the engine should be running smoothly and efficiently; if either a rich or lean condition exists it must be repaired as this may be the cause of the P219A being stored. Failure to do so could result in incorrect diagnosis of various issues with the vehicle.
In order to accurately diagnose a code P219A, it is necessary to have a diagnostic scanner, a digital volt/ohmmeter (DVOM), and an up-to-date source of reliable vehicle information on hand. The right tools are essential for properly diagnosing the problem in order to provide an optimal repair solution.
Taking the time to search for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) that match the stored codes, vehicle information (year, make, model, and engine), and symptoms exhibited can be a great way of saving time in diagnosing a problem. This information is often available through a vehicle’s source of information. If you find the right TSB then it could provide an efficient solution to your diagnosis.
The technician should then connect the scanner to the vehicle diagnostic port and retrieve all stored codes and pertinent freeze frame data, writing this information down in case the code proves to be an intermittent one. To complete the process, they must then clear the codes before taking a test drive until either the code is restored or until readiness mode has been achieved by the PCM.
If the PCM enters readiness mode at this point, the code may be more difficult to diagnose because it is intermittent. In this case, it would be necessary for the condition that caused P219A to be stored to worsen before an accurate diagnosis can be made. If the code is restored, however, then further steps should be taken in order to make a definitive diagnosis.
The source of vehicle information can provide a wide range of materials relating to the particular code and vehicle in question, such as connector face views, connector pinout charts, component locator charts, wiring diagrams and diagnostic flow charts. All these documents are invaluable for understanding how the code and vehicle interact with each other.
The technician should perform a visual inspection of the related wiring and connectors to ensure they are in good condition. If any damage such as cuts, burns, or wear is noticed, then the technician should repair or replace them accordingly. It is important for safety reasons that all wiring and connectors work correctly before proceeding with further tasks.
It is recommended that if the engine is running smoothly and the code P219A/P219B continues to be reset, the engine should be started and allowed to reach normal operating temperature. Furthermore, when idling (with either neutral or park selected on the transmission), a scanner should be connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port in order to observe oxygen sensor input data from within the data stream. To ensure quicker response times, it is important that only applicable information be included in this scan.
If the oxygen sensors are functioning normally, once the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) enters closed loop operation, voltage on pre-catalytic converter oxygen sensors will cycle continuously between 1 and 900 millivolts. Post-catalytic converter oxygen sensors also cycle between 1 and 900 millivolts but settle at a certain point and remain more stable than pre-catalytic converters. When an oxygen sensor fails to cycle adequately, it should be considered defective if the engine is in good working condition.
In most cases, rectifying this code will involve correcting a running engine that is either too rich or too lean. It is important to ensure that the right balance of fuel and air is present in the combustion chamber for optimal performance. To do this, an experienced technician may need to assess the vehicle’s current state and make adjustments accordingly. Additionally, they may need to take preventive measures such as replacing spark plugs and filters regularly or checking for any blockages in the exhaust system.
Мало того, что OBD2 ошибки работы двигателя или других электронных систем автомобиля не всегда на прямую указывают на неработающий элемент, но и в разных марках и моделях автомобилей одна и таже ошибка может возникать как следствие неисправности абсолютно разных элементов электронной системы.
Мы надеемся, с Вашей помощью, сформировать причино-следственную связь возникновения той или иной OBD2 ошибки у конкретного автомобиля (марка и модель). Как показал опыт если рассматривать определенную марка-модель автомобиля, то в подавляющем большинстве случаев причина ошибки одна и также.
Если ошибка указывает на неверные параметры (высокие или низкие значения) какого нибудь из датчиков или анализаторов, то вероятней всего этот элемент исправен, а проблему надо искать так сказать «выше по течению», в элементах работу которых анализирует датчик или зонд.
Если ошибка указывает на постоянно открытый или закрытый клапан, то тут надо подойти к решению вопроса с умом, а не менять бездумно этот элемент. Причин может быть несколько: клапан засорен, клапан заклинил, на клапан приходит неверный сигнал от других неисправных узлов.
Ошибки работы двигателя OBD2 и других систем автомобиля не всегда на прямую указывают на неработающий элемент. Сама по себе ошибка является косвенными данными о неисправности в системе, в некотором смысле подсказкой, и только в редких случаях прямым указанием на неисправный элемент, датчик или деталь. Ошибки (коды ошибок) полученные от прибора, сканера требуют правильной интерпретации информации, дабы не тратить время и деньги на замену работающих элементов автомобиля. Проблема зачастую кроется намного глубже чем кажется на первый взгляд. Это вызвано теми обстоятельствами, что информационные сообщения содержат, как было выше сказано, косвенную информацию о шарушении работы системы.
Вот пару общих примеров. Если ошибка указывает на неверные параметры (высокие или низкие значения) какого нибудь из датчиков или анализаторов, то вероятней всего этот элемент исправен, так как он анализирует (выдает некие параметры или значения), а проблему надо искать так сказать «выше по течению», в элементах работу которых анализирует датчик или зонд.
Если ошибка указывает на постоянно открытый или закрытый клапан, то тут надо подойти к решению вопроса с умом, а не менять бездумно этот элемент. Причин может быть несколько: клапан засорен, клапан заклинил, на клапан приходит неверный сигнал от других неисправных узлов.
Еще один момент который хотелось бы отметить — это специфика той или иной марки и модели. Поэтому узнав ошибку работы двигателя или дрогой системы Вашего автомобиля не спешите делать поспешных решений, а подойдите к вопросу комплексно.