Что означает ошибка SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
Это значит, что мы пытаемся выйти из цикла, которого нет
Это значит, что мы пытаемся выйти из цикла, которого нет
Ситуация: мы пишем опросник на Python, и нам важно, чтобы его мог пройти только совершеннолетний. Для этого мы добавляем в код такую логику:
- Спрашиваем про возраст.
- Смотрим, он больше 18 или нет.
- Если нет — останавливаем программу.
- Пишем дальше код, который будет работать, если участнику есть 18 лет и программа не остановилась.
На Python это выглядит так:
# запрашиваем возраст
age_txt = input('Введите свой возраст: ')
# переводим введённое значение в число
age = int(age_txt)
# если меньше 18 лет
if age < 18:
# выводим сообщение
print('Вы не можете участвовать в опросе')
# выходим из программы
break
# спрашиваем имя
name_txt = input('Как вас зовут: ')Вроде всё логично, но после запуска мы получаем ошибку:
❌ SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
Что это значит: в отличие от многих других языков, команда break в Python используется только для выхода из цикла, а не выхода из программы в целом.
Когда встречается: когда мы хотим выйти из программы в середине её работы, но не знаем как.
Что делать с ошибкой SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
Всё зависит от того, что вы хотите сделать.
Если вы хотите выйти из цикла, то break служит как раз для этого — нужно только убедиться, что всё в порядке с отступами. Например, здесь мы выйдем из цикла, как только переменная станет больше 9:
for i in range(10):
print(i)
if i > 8:
breakА если вы хотите закончить работу программы в произвольном месте, то нужно вместо break использовать команду exit(). Она штатно завершит все процессы в коде и остановит программу. Это как раз подойдёт для нашего примера с опросником — теперь программа остановится, если возраст будет меньше 18:
# запрашиваем возраст
age_txt = input('Введите свой возраст: ')
# переводим введённое значение в число
age = int(age_txt)
# если меньше 18 лет
if age < 18:
# выводим сообщение
print('Вы не можете участвовать в опросе')
# выходим из программы
exit()
# спрашиваем имя
name_txt = input('Как вас зовут: ')Вёрстка:
Кирилл Климентьев
Получите ИТ-профессию
В «Яндекс Практикуме» можно стать разработчиком, тестировщиком, аналитиком и менеджером цифровых продуктов. Первая часть обучения всегда бесплатная, чтобы попробовать и найти то, что вам по душе. Дальше — программы трудоустройства.
Начать карьеру в ИТ
Мне нужно создать Меню утилиты, чтобы при вводе 9 у меня открывалось второе меню, которое также запускалось заново при выборе какой либо функции, а не вылетало, но выдаёт ошибку D:>python 4ist1k.py
File «D:4ist1k.py», line 69
break
^
SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
Вот сам код:
clear = input("Выберите пункт: ")
#-Начало-функций-очистки
if clear == "1":
print('[!] Очистка файла...')
elif clear == "2":
print(wrn, "Очистка истории")
elif clear == "0":
break
else:
print("Вы ввели неправильное значение...")
Здесь без функций, чтобы было кратко
задан 2 дек 2020 в 17:17
6
break можно использовать только в цикле для досрочного прерывания цикла.
Чтобы прекратить выполнение условного оператора, надо обернуть его в функцию
user_clear = input("Выберите пункт: ")
def check_user_input(clear):
if clear == "1":
print('[!] Очистка файла...')
elif clear == "2":
print(wrn, "Очистка истории")
elif clear == "0":
return # завершает функцию
else:
print("Вы ввели неправильное значение...")
check_user_input(user_clear)
Чтобы выйти из программы можно использовать raise SystemExit(0)
ответ дан 2 дек 2020 в 17:33
gmangman
111 бронзовый знак
2
Hello coders!! In this article, we will be learning about the “break outside loop” loop error in Python. We will see its cause with some examples and will ultimately learn how to resolve this error. Let us now understand it in detail.
What does ‘break’ mean in Python?
The ‘break’ statement is used to instruct Python to exit from a loop. It is commonly used to exit a loop abruptly when some external condition is triggered. The break statement can be used in any type of loop – while loop and for loop.
n = 10
while n > 0:
print ('Value :', n)
n = n -1
if n == 5:
break
print ('Exiting the loop')
output:
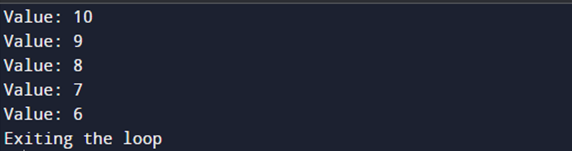
As we can see, when the value of the variable becomes 5, the condition for the break statement triggers and Python exits the loop abruptly.
SyntaxError: break outside loop in Python:
The purpose of a break statement is to terminate a loop abruptly by triggering a condition. So, the break statement can only be used inside a loop. It can also be used inside an if statement, but only if it is inside a loop. If one uses a break statement outside of a loop, then they will get the “SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop” error in their code.
n = 10
if n < 15:
print('The number is less than 15')
else:
break
output:
We can see that the error SyntaxError: break outside loop occurs. This is because we have used the break statement without any parent loop.
Resolution for SyntaxError: break outside loop in Python:
The cause of the above error is that the break statement can’t be used anywhere in a program. It is used only to stop a loop from executing further.
We need to remove the break statements in order to solve the error. An exception can replace it. We use exceptions to stop a program and provide an error message.
n = 20
if n < 15:
print('The number is less than 15')
else:
raise Exception("The number is not less than 15")
Output:

The code now returns an exception based on the given condition. When we use an exception, it stops the program from further execution( if triggered) and displays the error message.
If we want the program to continue further execution, we cam simply use a print statement.
n = 20
if n < 15:
print('The number is less than 15')
else:
print("The number is not less than 15")
Output:

Here, due to the use of print statement, the program does not stop from execution.
Difference between break, exit and return:
| BREAK | EXIT | RETURN |
| Keyword | System Call | Instruction |
| exit from a loop | exit from a program and return the control back to OS | return a value from a function |
Conclusion: Break Outside Loop Python
In this article, we discussed in detail the Python “break out of loop error.” We learned about using the break statement and saw the scene in which the said error can occur. So, to avoid it, we must remember to use the break statement within the loop only.
However, if you have any doubts or questions, do let me know in the comment section below. I will try to help you as soon as possible.
Happy Pythoning!

The break statement terminates the current loop and resumes execution at the next statement. You can only use a break statement inside a loop or an if statement. If you use a break statement outside of a loop, then you will raise the error “SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop”.
Table of contents
- SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
- What is SyntaxError?
- What is a Break Statement?
- Example: If Statement
- Solution
- Summary
SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
What is SyntaxError?
Syntax refers to the arrangement of letters and symbols in code. A Syntax error means you have misplaced a symbol or a letter somewhere in the code. Let’s look at an example of a syntax error:
number = 23
print()number print()number
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntaxThe ^ indicates the precise source of the error. In this case, we have put the number variable outside of the parentheses for the print function, and the number needs to be inside the parentheses to print correctly.
print(number)23What is a Break Statement?
Loops in Python allow us to repeat blocks of code. In cases, Sometimes conditions arise where you want to exit the loop, skip an iteration, or ignore a condition. We can use loop control statements to change execution from the expected code sequence, and a break statement is a type of loop control statement.
A break statement in Python brings the control outside the loop when an external condition is triggered. We can put an if statement that determines if a character is an ‘s‘ or an ‘i‘. If the character matches either of the conditions the break statement will run. We can use either a for loop or a while loop. Let’s look at an example where we define a string then run a for loop over the string.
string = "the research scientist"
for letter in string:
print(letter)
if letter == 's' or letter == 'i':
break
print("Out of the for loop")
t
h
e
r
e
s
Out of the for loopThe for loop runs until the character is an ‘s‘ then the break statement halts the loop. Let’s look at the same string example with a while loop.
i = 0
while True:
print(string[i])
if string[i] =='s' or string[i] == 'i':
break
i += 1
print(Out of the while loop")t
h
e
r
e
s
Out of the while loop We get the same result using the while loop.
Example: If Statement
Let’s look at an example where we write a program that checks if a number is less than thirty. We can use an input() statement to get input from the user.
number = int(input("Enter an appropriate number "))
Next, we can use an if statement to check whether the number is less than thirty.
if number ≺ 30:
print('The number is less than 30')
else:
breakSuppose the number is less than thirty, the program prints a message to the console informing us. Otherwise, a program will run a break statement. Let’s run the program and see what happens:
Enter an appropriate number: 50
break
^
SyntaxError: 'break' outside loopThe program returns the SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop because the break statement is not for breaking anywhere in a program. You can only use a break statement within a loop.
Solution
To solve this problem, we need to replace the break statement with an exception that stops the program if the number exceeds thirty and provides an exception message. Let’s look at the revised code.
number = int(input("Enter an appropriate"))
if number ≺ 30:
print('The number is less than 30')
else:
raise Exception("The number is not less than 30")We replaced the break statement with a raise Exception.
<meta charset="utf-8">Enter an appropriate number: 50
Exception Traceback (most recent call last)
2 print('The number is less than 30')
3 else:
----≻ 4 raise Exception('The number is greater than 30')
5
Exception: The number is greater than 30If the number is greater than thirty the program will raise an exception, which will halt the program.
Summary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! The error “SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop” occurs when you put a break statement outside of a loop. To solve this error, you can use alternatives to break statements. For example, you can raise an exception when a certain condition is met. You can also use a print() statement if a certain condition is met.
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!

✋ Update: This post was originally published on my blog decodingweb.dev, where you can read the latest version for a 💯 user experience. ~reza
Python raises “SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop” whenever it encounters a break statement outside a loop. The most common cases are using break within an if block (that’s not part of a loop) or when you accidentally use it instead of return to return from a function.
Here’s what the error looks like:
File /dwd/sandbox/test.py, line 2
break
^^^^^
SyntaxError: 'break' outside loop
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
The break statement is a control flow feature used to break out of the innermost loop. For instance, when you reach a specific value. That’s pretty much like the C language.
Based on Python syntax, the break keyword is only valid inside loops — for and while.
Here’s an example:
values = [7, 8, 9.5, 12]
for i in values:
# Break out of the loop if i > 10
if (i > 10):
break
print(i)
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
The above code iterates over a list and prints out the values less than 10. Once it reaches a value greater than 10, it breaks out of the loop.
How to fix SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop
The error «SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop» occurs under two scenarios:
- When using
breakinside anifblock that’s not part of a loop - When using
break(instead ofreturn) to return from a function
Let’s see some examples with their solutions.
When using break inside an if block that’s not part of a loop: One of the most common causes of «SyntaxError: ‘break’ outside loop» is using the break keyword in an if block that’s not part of a loop:
if item > 100
break # 🚫 SyntaxError: 'break' outside loop
# some code here
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
There’s no point in breaking out of an if block. If the condition isn’t met, the code isn’t executed anyway. The above code only would make sense if it’s inside a loop:
values = [7, 8, 9.5, 12]
for item in values:
if (item > 10):
break
print(i)
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Otherwise, it’ll be useless while being a SyntaxError too!
However, if you want to keep the if block for syntactical reasons, you can replace the break keyword with the pass keyword.
A pass statement does nothing in Python. However, you can always use it when a statement is required syntactically, but no action is needed.
When using break (instead of return) to return from a function: Another reason behind this error is to accidentally use the break keyword (instead of return) to return from a function:
def checkAge(age):
if (age < 12):
break # 🚫 SyntaxError: 'break' outside loop
# some code here
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
To return from a function, you should always use return (with or without a value):
def checkAge(age):
if (age <= 12):
return
# some code here
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Alright, I think it does it. I hope this quick guide helped you solve your problem.
Thanks for reading.
❤️ You might like:
- TabError: inconsistent use of tabs and spaces in indentation (Python)
- How to reverse a range in Python (with examples)
- Unindent does not match any outer indentation level error in Python (Fixed)